|
Size: 606
Comment:
|
Size: 6383
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 4: | Line 4: |
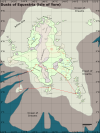
The State of Lancang is a constituent polity of the Earth Kingdom, governed by an indigenous prince with a nominal allegiance to the Earth King in Ba Sing Se. It is named for the great river system running down its Western valley, which arises in the highlands of Boshan and Lancang and empties into the gulf of Gaoling. The geography is mostly mountainous. Its indigenous inhabitants are the [[Avatar/Shanqi Villagers|Mountain-Air Villagers]] who are an earth nation who practice a form of the [[Avatar/Air Nomad Religion|Air Nomad religion]] taught to them by missionaries in late antiquity; they were historically the majority of the population, but their numbers have diminished. The economy is mostly agrarian and autarkic, with modest agricultural exports to the cities on the gulf and some textile production in the settlements. |
|
| Line 5: | Line 8: |
| Line 6: | Line 10: |
In prehistory, the highlands were sparsely inhabited by nomadic pastoralists of what anthropologists call the Carding Bow Culture, after a distinctive artifact of their material culture (a tool used to process the wool of their goatmarmot herds.) Little is known of the Carding Bow Culture, and they were assimilated by a different group of earthbending nomadic pastoralists migrating from the north of the Boshan plateau before literacy reached the region. The recorded history of the Lancang Valley, in the West of the state's present territory, dates to the time of the Di dynasty, though it had no connection to the North or Omashu and was rather part of the cultural sphere of Gaoling. The Lancang valley, in those days, was controlled by small city-states; they had little contact with those highland people they called "mountain barbarians." The coming of Air Nomad missionaries occurred in late antiquity. The Air Nomads introduced literacy to the highlands and actively, though peacefully, promoted their religion, as their restrained attitudes toward proselytism were yet to develop. Deciding that the highlands, though sparsely inhabited, could not pasture large sky bison herds sustainably, only a few Air Nomads actually stayed on the Boshan Plateau themselves, but they continued to have extensive cultural contact. The highland people came to be known as Shanqi (Mountain-Air) villagers, and began to develop more trade and cultural links with the Valley with the availability of sky bison and the introduction of the Gaoling shallowboat in the 1600s BG. |
|
| Line 7: | Line 16: |
In 1548 BG, the Kingdom of Zou invaded the Boshan plateau during [[Avatar/Zou-Gaoling War|a war with Gaoling]] over conflicting interests on the Southern coast. The highland peoples confederated to resist the invasion, electing the first Prince of Boshan, Mipham Tenzin, to organize the defense. The invasion was repelled, and the plateau thereafter cast off the suzerainty of Gaoling, which had been weakened by the war; the Boshan Principality even came to control the Lancang valley and its urban population. For the next several hundred hundred years, the Principality of Boshan, which extended into the present-day polities of Boshan, Lancang, and the Kingdom of Zou, remained independent, though at times paying tribute to Gaoling or Omashu, mostly the latter. Power was divided between the secular Prince, whose base of power was in the Lancang Valley, and the abbots of the great monasteries, whose received tithes and corvee from the Sanqi in the highlands. Over time, the Shanqi adopted more of a settled way of life, as they pivoted from subsistance agriculture to trading goatmarmot wool to the valley folk for food. The Principality was divided into roughly the modern states of Boshan and Lancang, mostly bloodlessly, over a theological dispute between the great monasteries, who disagreed about the obligation for laypeople to be vegetarian. In Boshan, vegetarianism remained optional; in Lancang, it became obligatory except for visitors. When the armies of the Ting dynasty invaded the South and united most of the modern Earth Kingdom, both of the principalities of Boshan and Lancang submitted to Earth King without violent resistance. |
|
| Line 8: | Line 22: |
When the Fire Nation attacked the Air Nomads, and began their systematic extermination, many survivors fled to Lancang and Boshan. This was a natural choice as both of these regions had large numbers of sympathetic coreligionists who were, at least theoretically, protected by the Earth Kingdom as its subjects. Unfortunately, this protection was not effective; the Fire Nation began raids into the plateau to target the surviving Air Nomads and anyone harboring them. Even Shanqi with no connection to the situation were sometimes suspected of being Air Nomads and killed by the raiders. Although the geography of the highlands provided some protection, the unwarlike Shanqi were unable to resist the Fire Nation. Earth Kingdom garrisons were understaffed and mostly concentrated in the Lancang valley, and only sporadically resisted the Fire Nation. The Prince of Lancang of the time, Gongzim Tenzin, turned collaborationist despite his nominal allegiance to the Earth Kingdom, and sent his own forces to find Air Nomads and turn them over to the Fire Nation in exchange for avoiding further devastating raids and the slaughter of those whose only connection to the Air Nomads was religious affinity. As a result of the Fire Nation raids and economic damage due to the loss of sky bison transport links, the population of Lancang has declined since its peak before the war, and become more urban. Many Mountain Air villagers have assimilated into the urban Lancang valley. Some of the great monasteries remain closed to this day. These institutions, targeted by the Fire Nation for their role in sheltering the refugees, were heavily damaged; many monastics fled or were martyred. |
<<Card: execution failed [local variable 'page' referenced before assignment] (see also the log)>>
Overview
The State of Lancang is a constituent polity of the Earth Kingdom, governed by an indigenous prince with a nominal allegiance to the Earth King in Ba Sing Se. It is named for the great river system running down its Western valley, which arises in the highlands of Boshan and Lancang and empties into the gulf of Gaoling. The geography is mostly mountainous. Its indigenous inhabitants are the Mountain-Air Villagers who are an earth nation who practice a form of the Air Nomad religion taught to them by missionaries in late antiquity; they were historically the majority of the population, but their numbers have diminished. The economy is mostly agrarian and autarkic, with modest agricultural exports to the cities on the gulf and some textile production in the settlements.
History
Antiquity
In prehistory, the highlands were sparsely inhabited by nomadic pastoralists of what anthropologists call the Carding Bow Culture, after a distinctive artifact of their material culture (a tool used to process the wool of their goatmarmot herds.) Little is known of the Carding Bow Culture, and they were assimilated by a different group of earthbending nomadic pastoralists migrating from the north of the Boshan plateau before literacy reached the region. The recorded history of the Lancang Valley, in the West of the state's present territory, dates to the time of the Di dynasty, though it had no connection to the North or Omashu and was rather part of the cultural sphere of Gaoling. The Lancang valley, in those days, was controlled by small city-states; they had little contact with those highland people they called "mountain barbarians."
The coming of Air Nomad missionaries occurred in late antiquity. The Air Nomads introduced literacy to the highlands and actively, though peacefully, promoted their religion, as their restrained attitudes toward proselytism were yet to develop. Deciding that the highlands, though sparsely inhabited, could not pasture large sky bison herds sustainably, only a few Air Nomads actually stayed on the Boshan Plateau themselves, but they continued to have extensive cultural contact. The highland people came to be known as Shanqi (Mountain-Air) villagers, and began to develop more trade and cultural links with the Valley with the availability of sky bison and the introduction of the Gaoling shallowboat in the 1600s BG.
Before the War
In 1548 BG, the Kingdom of Zou invaded the Boshan plateau during a war with Gaoling over conflicting interests on the Southern coast. The highland peoples confederated to resist the invasion, electing the first Prince of Boshan, Mipham Tenzin, to organize the defense. The invasion was repelled, and the plateau thereafter cast off the suzerainty of Gaoling, which had been weakened by the war; the Boshan Principality even came to control the Lancang valley and its urban population.
For the next several hundred hundred years, the Principality of Boshan, which extended into the present-day polities of Boshan, Lancang, and the Kingdom of Zou, remained independent, though at times paying tribute to Gaoling or Omashu, mostly the latter. Power was divided between the secular Prince, whose base of power was in the Lancang Valley, and the abbots of the great monasteries, whose received tithes and corvee from the Sanqi in the highlands. Over time, the Shanqi adopted more of a settled way of life, as they pivoted from subsistance agriculture to trading goatmarmot wool to the valley folk for food. The Principality was divided into roughly the modern states of Boshan and Lancang, mostly bloodlessly, over a theological dispute between the great monasteries, who disagreed about the obligation for laypeople to be vegetarian. In Boshan, vegetarianism remained optional; in Lancang, it became obligatory except for visitors. When the armies of the Ting dynasty invaded the South and united most of the modern Earth Kingdom, both of the principalities of Boshan and Lancang submitted to Earth King without violent resistance.
Since the War
When the Fire Nation attacked the Air Nomads, and began their systematic extermination, many survivors fled to Lancang and Boshan. This was a natural choice as both of these regions had large numbers of sympathetic coreligionists who were, at least theoretically, protected by the Earth Kingdom as its subjects. Unfortunately, this protection was not effective; the Fire Nation began raids into the plateau to target the surviving Air Nomads and anyone harboring them. Even Shanqi with no connection to the situation were sometimes suspected of being Air Nomads and killed by the raiders. Although the geography of the highlands provided some protection, the unwarlike Shanqi were unable to resist the Fire Nation. Earth Kingdom garrisons were understaffed and mostly concentrated in the Lancang valley, and only sporadically resisted the Fire Nation. The Prince of Lancang of the time, Gongzim Tenzin, turned collaborationist despite his nominal allegiance to the Earth Kingdom, and sent his own forces to find Air Nomads and turn them over to the Fire Nation in exchange for avoiding further devastating raids and the slaughter of those whose only connection to the Air Nomads was religious affinity.
As a result of the Fire Nation raids and economic damage due to the loss of sky bison transport links, the population of Lancang has declined since its peak before the war, and become more urban. Many Mountain Air villagers have assimilated into the urban Lancang valley. Some of the great monasteries remain closed to this day. These institutions, targeted by the Fire Nation for their role in sheltering the refugees, were heavily damaged; many monastics fled or were martyred.
Climate, Geography and Biology
Economy
Agriculture
Industry
Trade
Transportation
Culture and Anthropology
Ethnic Composition
Languages Spoken
Cultural and Religious Institutions
Arts, Fashion and Cuisine
Subdivisions and Politics
Capital